
Photostable Small-Molecule NIR-II Fluorescent Scaffolds that Cross the Blood−Brain Barrier for Noninvasive Brain Imaging
光稳定小分子NIR-II荧光支架穿过血液−脑屏障进行非侵入性脑成像
主讲人:赵桂玲
Journal of the American Chemical Society ( IF 16.383 ) Pub Date : 2022-12-13 , DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c11223
Abstract:
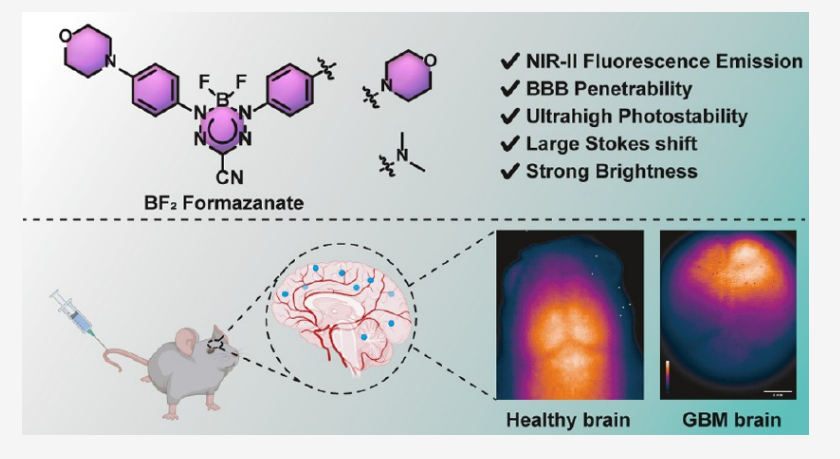
The second near-infrared (NIR-II, 1000−1700 nm)fluorescent probes have significant advantages over visible or NIR-I(600−900 nm) imaging for both depth of penetration and level of resolution. Since the blood−brain barrier (BBB) prevents most molecules from entering the central nervous system, NIR-II dyes with large molecular frameworks have limited applications for brain imaging. In this work, we developed a series of boron difluoride(BF2) formazanate NIR-II dyes, which had tunable photophysical properties, ultrahigh photostability, excellent biological stability,and strong brightness. Modulation of the aniline moiety of BF2 formazanate dyes significantly enhances their abilities to cross the BBB for noninvasive brain imaging. Furthermore, the intact mouse
brain imaging and dynamic dye diffusion across the BBB were monitored using these BF2 formazanate dyes in the NIR-II region. In murine glioblastoma models, these dyes can differentiate tumors from normal brain tissues. We anticipate that this new type of small molecule will find potential applications in creating probes and drugs relevant to theranostic for brain pathologies.
摘要:
第二种近红外(NIR-II,1000−1700nm)荧光探针在穿透深度和分辨率方面均比可见光或NIR-I(600−900nm)成像具有显著优势。由于血−脑屏障(BBB)阻止大多数分子进入中枢神经系统,具有大分子框架的NIR-II染料在脑成像中的应用有限。在这项工作中,我们开发了一系列二氟化硼(BF2)甲醛酸NIR-II染料,它们具有可调的光物理性质、超高的光稳定性、优异的生物稳定性和较强的亮度。调节BF2正甲酸染料的苯胺部分显著提高了它们穿过血脑屏障进行无创脑成像的能力。此外,使用NIR-II区域的BF2甲酸染料监测完整的小鼠大脑成像和血脑屏障内的动态染料扩散。在小鼠胶质母细胞瘤模型中,这些染料可以区分肿瘤和正常的脑组织。我们预计,这种新型的小分子将在创建与脑病理治疗相关的探针和药物方面找到潜在的应用。

