
A general strategy for detection of tumor-derived extracellular vesiclemicroRNAs using aptamer-mediated vesicle fusion
利用适体介导的囊泡融合检测肿瘤来源的细胞外囊泡微小RNA的一般策略
主讲人:刘清源
ELSEVIER |Available online 27 August2022|pages:1748-0132(2022)|doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101599|
Abstract
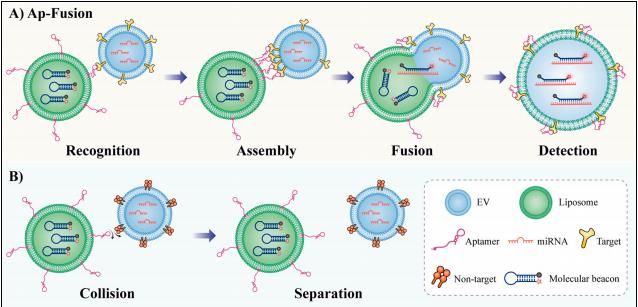
Extracellular vesicle (EV) microRNAs (miRNAs) derived from tumors are important biomarkers for clinical diagnosis and disease treatment monitoring. However, the need to lyse EV makes most methods for detecting tumor derived EVmiRNA expensive, labor-intensive, and time-consuming. Inspired by natural vesicle transport, we have developed a universal strategy for in situ detection of tumor derived EVmiRNA using aptamer mediated selective fusion (Apt fusion). Taking advantage of the high selectivity, speed, and versatility of AptFusion, this method demonstrated significant sensitivity and selectivity to tumor derived EVmiRNA in a non lysis manner using conventional flow cytometry. Using this method, the level of miR-21 in PD-L1 positive EV was quantified, and it was found that it can effectively distinguish between cancer patients and healthy individuals; In addition, for the first time, miR-21 in PD-L1 positive EV was found to be associated with tumor burden. Overall, Apt Fusion has great potential in detecting tumor derived EVmiRNAs and expanding the detection of EV multi molecular components, providing a new approach for cancer diagnosis and immunotherapy response monitoring.
摘要
肿瘤来源的细胞外囊泡(EV)微RNA(miRNA)是临床诊断和疾病治疗监测的重要生物标志物。然而,裂解EV的需要使得大多数检测肿瘤衍生EVmiRNA的方法昂贵、劳动密集且耗时。受自然囊泡转运的启发,我们在此开发了一种使用适配体介导的选择性融合(Apt-fusion)原位检测肿瘤衍生的EVmiRNA的通用策略。利用AptFusion的高选择性、快速和通用性的优势,该方法使用常规流式细胞术以无裂解的方式对肿瘤衍生的EVmiRNA表现出显著的敏感性和选择性。利用该方法,对PD-L1阳性EV中miR-21的水平进行了量化,发现其可以有效区分癌症患者和健康人;此外,首次发现PD-L1阳性EV中的miR-21与肿瘤负荷相关。总的来说,Apt-Fusion在检测肿瘤衍生EVmiRNAs和扩大EV多分子成分检测方面具有巨大潜力,为癌症诊断和免疫治疗反应监测提供了新的途径。

