
Rapid Isolation and Multiplexed Detection of Exosome Tumor Markers Via Queued Beads Combined with Quantum Dots in a Micro-array
微阵列快速分离肿瘤标记物外泌体的多路检测
主讲人:赵月月
Nano-Micro Letters丨Published:2019 Jul 16丨 Issue Date: 2019 Jun 10 丨 Pages: 59 :1-12 丨DOI: 10.1007/s40820-019-0285-x
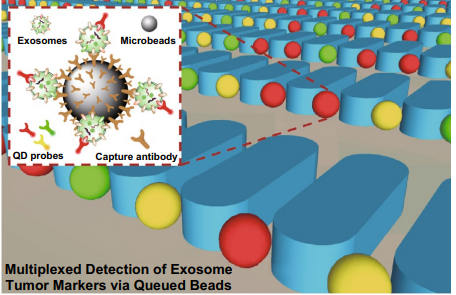
Abstract:
Tumor-derived exosomes are actively involved in cancer progression and metastasis and have emerged as a promising marker for cancer diagnosis in liquid biopsy. Because of their nanoscale size, complex biogenesis, and methodological limitations related to exosome isolation and detection, advancements in their analysis remain slow. Microfuidic technology ofers a better analytic approach compared with conventional methods. Here, we developed a bead-based microarray for exosome isolation and multiplexed tumor marker detection. Using this method, exosomes are isolated by binding to antibodies on the bead surface, and tumor markers on the exosomes are detected through quantum dot (QD) probes. The beads are then uniformly trapped and queued among micropillars in the chip. This design benefts fuorescence observation by dispersing the signals into every single bead, thereby avoiding optical interference and enabling more accurate test results. We analyzed exosomes in the cell culture supernatant of lung cancer and endothelial cell lines, and diferent lung cancer markers labeled with three QD probes were used to conduct multiplexed detection of exosome surface protein markers. Lung cancer-derived samples showed much higher (~sixfold–tenfold) fuorescence intensity than endothelial cell samples, and diferent types of lung cancer samples showed distinctive marker expression levels. Additionally, using the chip to detect clinical plasma samples from cancer patients showed good diagnostic power and revealed a well consistency with conventional tests for serological markers. These results provide insight into a promising method for exosome tumor marker detection and early-stage cancer diagnosis.
摘要:
肿瘤来源的外泌体积极参与癌症的进展和转移,已成为液体活检诊断的一种有前途的标志物。由于它们的纳米级大小、复杂的生物发生以及与外泌体分离和检测相关的方法的局限性,它们的分析进展仍然缓慢。微流控技术比传统方法具有更好的分析方法。在这里,我们开发了一种基于珠子的微阵列,用于外泌体分离和多路肿瘤标记物检测。利用这种方法,通过与珠子表面的抗体结合来分离出外泌体,并通过量子点(QD)探针检测外泌体上的肿瘤标记物。然后,这些珠子被均匀地捕获在芯片中的微柱之间。这种设计通过将信号分散到每一个珠子中,有利于荧光检测,从而避免了光学干扰,得到更准确的测试结果。我们分析了肺癌和内皮细胞系细胞培养上清中的外泌体,并使用三种QD探针标记的不同肺癌标记物对外泌体表面蛋白标记物进行多路检测。肺癌来源的样本的荧光强度更高(~6倍-10倍),不同类型的肺癌样本表现出独特的标记物表达水平。此外,使用该芯片检测来自癌症患者的临床血浆样本显示出良好的诊断能力,并与常规的血清学标记物检测具有良好的一致性。这些结果为外泌体肿瘤标志物的检测和早期癌症的诊断提供了一种很有前途的方法。

